Early Ideas of the Age of the Earth
1654
the Earth was created October 26, 4004 BC, 9:00 am
Earth was thus 6000 years old.
Led to the Doctrine of Catastrophism:
Earth was shaped by series of giant disasters.
Had to fit many processes into a short time scale.
1770's, 1780's
James Hutton, Father of Geology (Scotland) 1726-1797.
Published Theory of the Earth in 1785.
Hadrian's Wall built by Romans, after 1500 years no change. Suspected that Earth was then much older.
1897
Quantitative Scientific Methods
Lord Kelvin assumed that the Earth was originally molten and calculated a date based on cooling through conduction and radiation.Age of Earth was calculated to be about 24-40 million years.
1899 - 1901
Age of Ocean = Total salt in oceans (in grams) divided by rate of salt added (grams per year)
Age of Earth was calculated to be 90-100 million years.
Radiometric Dating
or,
How do we determine the age of a rock?
Principles of Radiometric Dating
Naturally-occurring radioactive materials break down into other materials at known rates. This is known as radioactive decay.Radioactive parent elements decay to stable daughter elements.
Radioactivity was discovered in 1896 by Henri Becquerel. In 1905, Rutherford and Boltwood used the principle of radioactive decay to measure the age of rocks and minerals (using Uranium decaying to produce Helium. Uranium decay produces He, leading to a date of 500 million years. Boltwood suspected that lead was the stable end product of the decay of uranium. In 1907, Boltwood dated a sample of urnanite based on uranium/lead ratios. Published the age of a sample of urananite based on Uranium-Lead dating. Date was 1.64 billion years. Amazingly, this was all done before isotopes were known, and before the decay rates were known accurately.
The invention of the MASS SPECTROMETER after World War I (post-1918) led to the discovery of more than 200 isotopes.
Many radioactive elements can be used as geologic clocks. Each radioactive element decays at its own nearly constant rate. Once this rate is known, geologists can estimate the length of time over which decay has been occurring by measuring the amount of radioactive parent element and the amount of stable daughter elements.
Radioactive parent isotopes and their stable daughter products
Radioactive Parent |
Stable Daughter |
|---|---|
Potassium 40 |
Argon 40 |
Rubidium 87 |
Strontium 87 |
Thorium 232 |
Lead 208 |
Uranium 235 |
Lead 207 |
Uranium 238 |
Lead 206 |
Carbon 14 |
Nitrogen 14 |
In the above table, note that the number is the mass number (the
total number of protons plus neutrons).
Note that the mass number may vary for an element, because of a differing
number of neutrons.
Elements with various numbers of neutrons are called isotopes of
that element.
Each radioactive isotope has its own unique half-life.
A half-life is the time it takes for half of the parent radioactive
element to decay to a daughter product.
Half Lives for Radioactive Elements
Radioactive Parent |
Stable Daughter |
Half life |
|
|---|---|---|---|
Potassium 40 |
Argon 40 |
1.25 billion yrs |
|
Rubidium 87 |
Strontium 87 |
48.8 billion yrs |
|
Thorium 232 |
Lead 208 |
14 billion years |
|
Uranium 235 |
Lead 207 |
704 million years |
|
Uranium 238 |
Lead 206 |
4.47 billion years |
|
Carbon 14 |
Nitrogen 14 |
5730 years |
Radioactive decay occurrs at a constant exponential or geometric rate.
The rate of decay is proportional to the number of parent atoms
present.
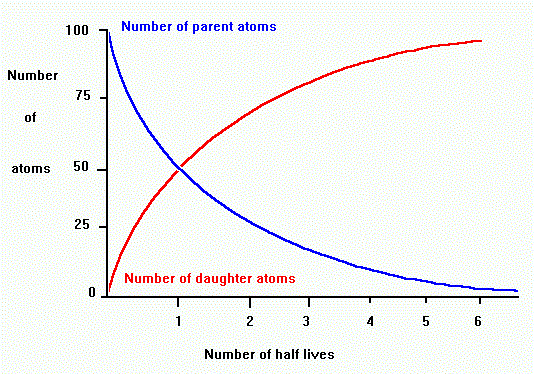
The proportion of parent to daughter atoms tells us the number of half-lives,
which we can use to find the age in years.
For example, if there are equal amounts of parent and daughter, then one
half-life has passed.
If there is three times as much daughter as parent, then two half-lives
have passed. (see graph, above)
Radioactive decay occurs by releasing particles and energy.
Uranium decays producing subatomic particles, energy, and lead.
As uranium-238 decays to lead, there are 13 intermediate radioactive daughter products formed (including radon, polonium, and other isotopes of uranium), and 8 alpha particles and 6 beta particles released. There are three types of subatomic particles involved:
- Alpha particles
large, easily stopped by paper
charge = +2
mass = 4 - Beta particles
penetrate hundreds of times farther than alpha particles, but easily stopped compared with neutrons and gamma rays.
charge = -1
mass = negligible
- neutrons
highly penetrating
no charge
mass = 1
-
Highly penetrating electromagnetic radiation. Photons (light).
No charge or mass.
Can penetrate concrete. Lead shield can be used.
So how does Carbon-14 dating work?
- Cosmic rays from the sun strike Nitrogen 14 atoms in the
atmosphere and cause them to turn into radioactive Carbon 14,
which combines with oxygen to form radioactive carbon dioxide.
- Living things are in equilibrium with the atmosphere, and the
radioactive carbon dioxide is absorbed and used by plants. The
radioactive carbon dioxide gets into the food chain and the carbon
cycle.
- All living things contain a constant ratio of Carbon 14 to
Carbon 12. (1 in a trillion).
- At death, Carbon 14 exchange ceases and any Carbon 14 in the
tissues of the organism begins to decay to Nitrogen 14, and is not
replenished by new C-14.
- The change in the Carbon 14 to Carbon 12 ratio is the basis for
dating.
- The half-life is so short (5730 years) that this method can only be used on materials less than 70,000 years old. Archaeological dating uses this method.) Also useful for dating the Pleistocene Epoch (Ice Ages).
- Assumes that the rate of Carbon 14 production (and hence the amount of cosmic rays striking the Earth) has been constant (through the past 70,000 years).